The vibrant economic landscape of the UAE, particularly its numerous Free Zones, offers unparalleled opportunities for businesses. However, operating within these special economic areas comes with unique regulatory requirements, most notably the mandatory external audit. For companies navigating this complex terrain, understanding the specific audit nuances of Free Zones like DMCC, JAFZA, DIFC, IFZA, DWC, and RAKEZ is not just a compliance obligation but a strategic imperative. This comprehensive guide, brought to you by ProAct, a leading provider of expert auditing and financial services in the UAE, delves deep into the intricacies of Free Zone external audits in 2025 and beyond, ensuring your business remains compliant and thrives.
Why are Free Zone External Audits So Critical for Your UAE Business?
Operating in a UAE Free Zone grants businesses significant advantages, including 100% foreign ownership, full repatriation of profits, and often, zero corporate and personal income tax (historically). However, these benefits are contingent upon strict adherence to Free Zone authority regulations. A mandatory external audit serves as a crucial mechanism for authorities to ensure financial transparency, compliance with Free Zone rules, and increasingly, adherence to economic substance regulations. Failure to comply can lead to hefty penalties, license suspension, or even revocation.
The Evolving Landscape of UAE Free Zone Audits
The year 2025 brings with it continued evolution in the regulatory environment. With the introduction of Corporate Tax in the UAE, the scope and scrutiny of Free Zone external audits have broadened. Businesses must now demonstrate not just financial accuracy but also genuine operational presence and alignment with their licensed activities. This shift necessitates a more comprehensive and strategic approach to audit preparedness.
Key Takeaway: Free Zone external audits are vital for compliance, risk mitigation, and maintaining your business license in the UAE.
Understanding the Varying Audit Requirements Across Prominent UAE Free Zones
While the overarching objective of external audits remains consistent, the specific requirements can differ significantly between Free Zones. This variability necessitates a nuanced understanding of each authority’s mandates.
DMCC (Dubai Multi Commodities Centre) Audit Requirements
As one of the largest and fastest-growing Free Zones, DMCC companies are subject to stringent audit requirements. DMCC generally mandates annual external audits by a DMCC-approved auditor. They often require financial statements to be prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or IFRS for SMEs.
- Financial Reporting Standards: IFRS or IFRS for SMEs.
- Submission Deadline: Typically within 180 days of the financial year-end.
- Key Focus Areas: Compliance with DMCC regulations, economic substance requirements, and adherence to tax laws.
JAFZA (Jebel Ali Free Zone Authority) Audit Specifics
JAFZA, a premier industrial and logistics hub, also requires annual external audits. JAFZA’s focus extends to ensuring that companies adhere to their operational licenses and maintain proper accounting records.
- Financial Reporting Standards: Primarily IFRS.
- Submission Deadline: Varies but generally within three to six months of the financial year-end.
- Key Focus Areas: Verification of commercial activities, adherence to operational guidelines, and proper inventory management for industrial companies.
DIFC (Dubai International Financial Centre) Audit Framework
DIFC, a leading global financial hub, has some of the most robust and sophisticated audit requirements. Companies operating here are often regulated by the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), which imposes high standards for financial reporting and corporate governance.
- Financial Reporting Standards: Strictly IFRS.
- Submission Deadline: Typically within 4 months of the financial year-end for DFSA-regulated entities.
- Key Focus Areas: Corporate governance, risk management frameworks, compliance with DFSA regulations, and anti-money laundering (AML) protocols.
IFZA (International Free Zone Authority) Audit Guidelines
IFZA, known for its efficiency and ease of setup, also requires an annual audit for its companies. While perhaps less stringent than DIFC, adherence to their regulations is crucial.
- Financial Reporting Standards: IFRS or IFRS for SMEs.
- Submission Deadline: Generally within 90 days of the financial year-end.
- Key Focus Areas: Verification of business activities, capital adequacy, and overall financial health.
DWC (Dubai World Central / Dubai South) Audit Mandates
DWC, encompassing Al Maktoum International Airport and various logistics and business districts, requires its entities to undergo annual external audits.
- Financial Reporting Standards: IFRS or IFRS for SMEs.
- Submission Deadline: Typically within 90-120 days of the financial year-end.
- Key Focus Areas: Operational efficiency, compliance with DWC master plan, and economic substance.
RAKEZ (Ras Al Khaimah Economic Zone) Audit Rules
RAKEZ, a rapidly growing Free Zone offering diverse business solutions, also mandates annual external audits for its licensees.
- Financial Reporting Standards: IFRS or IFRS for SMEs.
- Submission Deadline: Usually within 90 days of the financial year-end.
- Key Focus Areas: Verification of license activities, financial stability, and adherence to RAKEZ specific regulations.
ProAct Insight: Navigating these diverse requirements can be a daunting task for businesses. ProAct’s specialized Free Zone audit team possesses in-depth knowledge of each authority’s specific mandates, ensuring tailored and compliant audit solutions.
Free UAE Free Zone Audit Checklist: Is Your Business Audit-Ready?”
Download ProAct’s UAE Free Zone Audit Checklist to identify requirements to stay Audit-Ready.
Click Here! to download
If you need to know more details about ProAct’s Freezone Auditing Services in the UAE – Contact us now!
Specific Financial Reporting Standards Mandated by Each Free Zone Authority
The foundation of any external audit lies in the financial statements, which must be prepared according to specific reporting standards. In the UAE Free Zones, IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) or IFRS for SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Entities) are the most commonly accepted frameworks.
IFRS vs. IFRS for SMEs: What’s the Difference?
- IFRS (Full IFRS): This comprehensive set of accounting standards is designed for publicly accountable entities and larger, more complex businesses. It provides detailed guidance on recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of financial transactions.
- IFRS for SMEs: A simplified version of Full IFRS, specifically designed for small and medium-sized entities that do not have public accountability. It reduces the complexity and disclosure requirements, making it more manageable for smaller businesses while still ensuring high-quality financial reporting.
Table: Financial Reporting Standards Across Key UAE Free Zones
| Free Zone Authority | Primary Financial Reporting Standard | Notes |
| DMCC | IFRS or IFRS for SMEs | Depending on company size and complexity |
| JAFZA | IFRS | Strong emphasis on full IFRS compliance |
| DIFC | IFRS | Regulated entities often require full IFRS |
| IFZA | IFRS or IFRS for SMEs | Common for startups and smaller enterprises |
| DWC | IFRS or IFRS for SMEs | Varies based on entity’s nature of business |
| RAKEZ | IFRS or IFRS for SMEs | Generally allows IFRS for SMEs for smaller companies |
Understanding which standard applies to your business is the first step towards a smooth audit process. ProAct’s expert accounting services can help you prepare your financial statements in strict compliance with the relevant IFRS framework, setting the stage for a seamless audit.
Documentation and Timelines Unique to Free Zone External Audits
Efficient audit preparation hinges on meticulous documentation and strict adherence to submission timelines. Each Free Zone authority has specific requirements that businesses must be aware of.
Essential Documentation for Your Free Zone Audit
While the exact list may vary, common documentation required for a Free Zone external audit includes:
- Audited Financial Statements: Signed and stamped by the external auditor.
- Trial Balance: For the audit period.
- General Ledger: Detailing all transactions.
- Bank Statements and Reconciliations: For all company bank accounts.
- Sales and Purchase Invoices: Supporting revenue and expense transactions.
- Payroll Records: Including salary certificates, WPS reports (if applicable).
- Fixed Asset Register: Detailing company assets.
- Company Trade License: Current and valid.
- Memorandum of Association (MOA) / Articles of Association (AOA): And any amendments.
- Board Resolutions: Related to significant financial decisions.
- Contracts and Agreements: With major suppliers, customers, and employees.
- VAT Returns and Records: If registered for VAT.
- ESR Notification and Report: If subject to Economic Substance Regulations.
- Corporate Tax Registration and Records: As applicable from June 2023.
Critical Timelines for Free Zone Audit Submissions
Missing submission deadlines can lead to penalties and complicate license renewal. While specific dates can vary, here are general guidelines:
- Financial Year-End: Most companies in the UAE follow a financial year ending on December 31st.
- Audit Completion: Generally, within 3 months of the financial year-end.
- Submission to Free Zone Authority: Typically within 90 to 180 days of the financial year-end, depending on the Free Zone.
Example Scenario: A DMCC company with a December 31st financial year-end typically needs to submit its audited financial statements by June 30th of the following year. ProAct works diligently with clients to establish a clear timeline and ensure all documentation is prepared and submitted well in advance of deadlines.
Strategic Tip: Proactive preparation is key. Begin gathering your documents and engaging with your auditors well before your financial year-end.

Challenges and Nuances of Auditing Free Zone Entities
Auditing Free Zone entities presents specific challenges that require specialized expertise. These go beyond standard financial verification and delve into the unique operational and regulatory environment of these zones.
Related Party Transactions within Free Zones
Transactions between related parties (e.g., a Free Zone entity and its mainland parent company, or another Free Zone entity owned by the same group) are common. However, these transactions require careful scrutiny during an audit due to potential transfer pricing implications and the risk of non-arm’s length dealings. Auditors assess:
- Arm’s Length Principle: Are transactions conducted at market rates as if they were between independent parties?
- Proper Documentation: Are all related party transactions adequately documented and justified?
- Disclosure: Are all related party transactions properly disclosed in the financial statements?
Specific Free Zone Regulations and Bylaws
Each Free Zone has its own set of specific regulations, bylaws, and circulars that can impact financial reporting and operational aspects. Auditors specializing in Free Zones are abreast of these nuances, ensuring compliance that a general auditor might overlook. This includes rules related to:
- Share Capital Requirements: Minimum capital requirements and maintenance.
- Leasing and Property Regulations: Specific rules for office or warehouse leases.
- Visa and Employee Regulations: Compliance with Free Zone specific labor laws.
- Specific Industry Regulations: For specialized Free Zones like Dubai Healthcare City or Dubai Media City.
Case Study: A client, a trading company in JAFZA, was unaware of a recent circular regarding the re-classification of certain trading activities. ProAct’s audit team, being deeply familiar with JAFZA regulations, identified this during the audit planning phase. We advised the client on the necessary adjustments to their internal processes and disclosures, preventing potential non-compliance penalties.”
How External Auditors Interact with Free Zone Authorities
The relationship between external auditors and Free Zone authorities is one of professional oversight and information exchange. Auditors act as independent verifiers, providing assurance to the authorities regarding the financial health and compliance of licensed entities.
Role of Approved Auditors
Most Free Zones maintain a list of “approved auditors.” Companies are generally required to appoint an auditor from this pre-vetted list. This ensures that the auditing firms possess the necessary qualifications, experience, and understanding of the Free Zone’s specific regulatory framework.
Information Sharing and Reporting
Auditors submit the audited financial statements directly to the respective Free Zone authority. In some cases, authorities may engage in direct communication with auditors for clarifications or additional information, particularly during compliance checks or investigations.
Facilitating License Renewals and Compliance Checks
A clean audit report is often a prerequisite for timely license renewal. The audit process also serves as a critical compliance check, ensuring that the Free Zone entity is adhering to all statutory and regulatory requirements, including those related to corporate governance, anti-money laundering (AML), and economic substance.
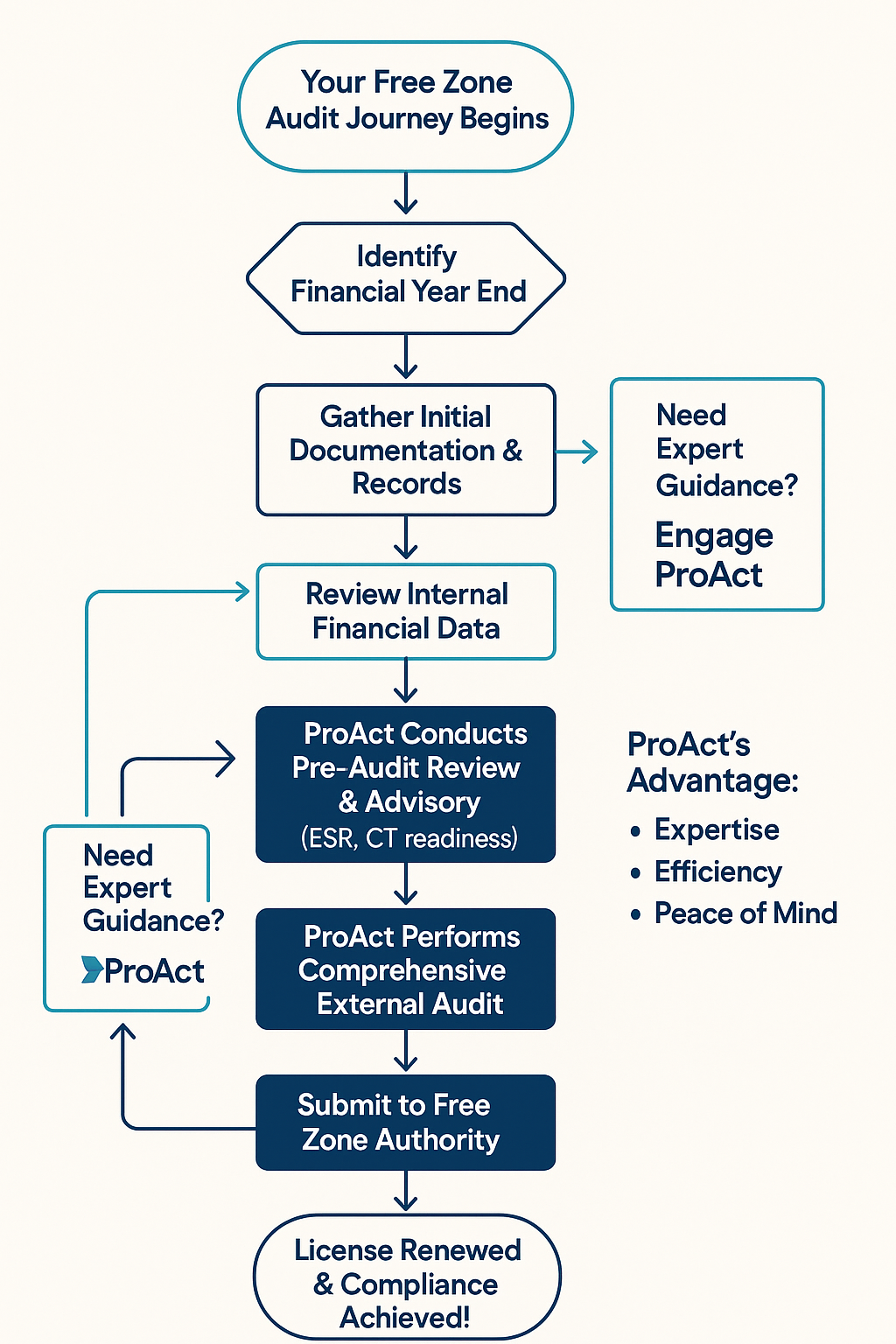
Expert Tip: A strong, collaborative relationship between your company, your internal finance team, and your external auditors streamlines the entire process, fostering transparency and trust with the Free Zone authorities.
Impact of Corporate Tax on Free Zone Entities and Their External Audit Scope
The introduction of Corporate Tax in the UAE (effective from financial years beginning on or after June 1, 2023) has significantly reshaped the financial landscape for Free Zone entities and, consequently, their external audit scope.
Corporate Tax Implications for Free Zones
While many Free Zone entities may enjoy a 0% Corporate Tax rate on qualifying income, this is not automatic. The Corporate Tax Law outlines specific conditions that must be met to qualify for Free Zone person status and the preferential tax rate. These conditions often relate to:
- Qualifying Income: Only income derived from qualifying activities and transactions may be subject to the 0% rate.
- Mainland UAE Income: Income derived from mainland UAE customers or activities may be subject to the standard 9% corporate tax rate.
- Compliance with ESR: Meeting Economic Substance Regulations is a key prerequisite for maintaining Free Zone status for Corporate Tax purposes.
- Maintenance of Adequate Substance: Demonstrating genuine business activities and substance within the Free Zone.
Expanded Audit Scope Due to Corporate Tax
External auditors now play a more critical role in verifying Corporate Tax compliance for Free Zone entities. The audit scope has expanded to include:
- Verification of Qualifying Income: Assessing whether income streams meet the criteria for the 0% tax rate.
- Segregation of Income: Ensuring proper segregation of qualifying and non-qualifying income.
- Tax Grouping Considerations: If part of a tax group, assessing compliance with grouping rules.
- Taxable Base Calculation: Reviewing the calculation of taxable income for non-qualifying activities.
- Deductibility of Expenses: Scrutinizing expenses to ensure they are deductible for corporate tax purposes.
- Review of Corporate Tax Returns: Providing assurance on the accuracy of filed Corporate Tax returns.
- Transfer Pricing Documentation: Greater scrutiny on related party transactions and transfer pricing policies in light of Corporate Tax regulations.
This increased complexity underscores the need for auditors with specialized tax knowledge relevant to Free Zone operations. ProAct’s integrated approach combines auditing expertise with comprehensive tax advisory, offering a holistic solution for your Free Zone entity.
Free UAE Free Zone Audit Checklist: Is Your Business Audit-Ready?”
Download ProAct’s UAE Free Zone Audit Checklist to identify requirements to stay Audit-Ready.
Click Here! to download
Choosing an External Audit Firm with Specialized Free Zone Expertise
The selection of an external audit firm is a strategic decision that can significantly impact your business’s compliance, efficiency, and financial health. For Free Zone entities, specialized expertise is non-negotiable.
Why General Auditors Are Not Enough for Free Zone Entities
While a general auditor might understand basic accounting principles, they often lack the nuanced understanding of:
- Specific Free Zone Bylaws: Each Free Zone has unique regulations that can affect financial reporting and operations.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: The rapid changes in UAE regulations, including ESR and Corporate Tax, require up-to-the-minute knowledge.
- Industry-Specific Nuances: Specialized Free Zones (e.g., media, healthcare, logistics) have unique operational and financial considerations.
- Interactions with Authorities: Familiarity with the specific processes and expectations of each Free Zone authority.
Key Qualities to Look for in a Free Zone Audit Firm
When evaluating audit firms, consider the following:
- Approved Status Across Major Free Zones: Ensure the firm is on the approved list of your specific Free Zone authority (e.g., DMCC approved auditors, JAFZA approved auditors).
- In-depth Knowledge of UAE Regulations: Beyond basic audit principles, look for expertise in UAE Commercial Companies Law, IFRS, VAT Law, ESR, and the new Corporate Tax Law. Our team comprises seasoned professionals with deep regulatory insight.
- Specialization in Free Zone Operations: The firm should demonstrate a track record of successfully auditing businesses similar to yours within Free Zones. ProAct’s portfolio is rich with diverse Free Zone clients.
- Proactive and Advisory Approach: A good auditor doesn’t just check boxes; they provide insights, identify potential risks, and offer strategic advice for improvement. We take a consultative approach, adding value beyond compliance.
- Technology Integration: Modern audit firms leverage technology for efficiency, data analytics, and secure document exchange. ProAct utilizes cutting-edge audit software to enhance accuracy and speed.
- Transparent Fee Structure: Clear and upfront pricing without hidden costs. ProAct believes in transparent and fair engagements.
- Client Testimonials and Reputation: Look for positive feedback and a strong reputation in the market. Our client success stories speak volumes about our commitment and expertise.
Don’t leave your Free Zone audit to chance. Partner with a firm that understands the intricacies of your environment. Contact ProAct today for a free consultation and discover how our specialized Free Zone audit services can empower your business.
20 Detailed FAQs on Free Zone External Audits in UAE (2025)
1. What is a Free Zone External Audit in UAE?
A Free Zone external audit in the UAE is a mandatory, independent examination of a Free Zone company’s financial statements and records. Its purpose is to ensure compliance with the specific regulations of the respective Free Zone authority, UAE laws (such as the Corporate Tax Law), and international accounting standards like IFRS. This audit provides assurance to stakeholders and the authority about the accuracy and fairness of the company’s financial reporting.
2. Is an external audit mandatory for all companies in UAE Free Zones?
Yes, an external audit is generally mandatory for all companies operating in UAE Free Zones, regardless of their size or activity, as a prerequisite for license renewal. Specific requirements and deadlines may vary slightly between Free Zones (e.g., DMCC, JAFZA, DIFC), but the obligation to undergo an annual audit remains a universal mandate.
3. How often do Free Zone companies need to conduct an external audit?
Free Zone companies are typically required to conduct an external audit annually, coinciding with their financial year-end. The audited financial statements must then be submitted to the relevant Free Zone authority within a stipulated timeframe, usually between 90 to 180 days from the financial year-end.
4. What are the common financial reporting standards used in UAE Free Zone audits?
The most common financial reporting standards used in UAE Free Zone audits are International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or IFRS for Small and Medium-sized Entities (IFRS for SMEs). The specific standard applicable to your company depends on the Free Zone authority’s requirements and the size/nature of your business. For instance, DIFC often requires full IFRS.
5. What documents are required for a Free Zone audit in the UAE?
For a Free Zone audit, you will typically need audited financial statements, trial balance, general ledger, bank statements and reconciliations, sales and purchase invoices, payroll records, fixed asset register, current trade license, Memorandum/Articles of Association, board resolutions, relevant contracts, VAT returns (if applicable), and Economic Substance Regulation (ESR) notifications/reports.
6. Can any auditor conduct a Free Zone audit, or do they need to be approved?
No, not just any auditor can conduct a Free Zone audit. Most UAE Free Zone authorities maintain a list of approved auditors. Companies are required to appoint an external audit firm from this list to ensure they possess the necessary qualifications, experience, and understanding of the Free Zone’s specific regulatory framework.
7. What is the deadline for submitting audited financial statements to Free Zone authorities?
The deadline for submitting audited financial statements to Free Zone authorities varies but typically ranges from 90 days to 180 days after the company’s financial year-end. For example, DMCC usually requires submission within 180 days, while JAFZA may allow up to 150 -180 days. It’s crucial to confirm the exact deadline with your specific Free Zone authority.
8. What happens if a Free Zone company fails to submit its audited financial statements on time?
Failure to submit audited financial statements on time to a Free Zone authority can result in significant penalties, including fines, suspension of your trade license, or even revocation of your license. It can also delay your license renewal process. ProAct helps companies avoid such penalties through timely and efficient audit services.
9. How has the new UAE Corporate Tax Law impacted Free Zone audits?
The new UAE Corporate Tax Law, effective from June 2023, has expanded the scope of Free Zone audits. Auditors now need to verify whether the Free Zone entity meets the conditions for the 0% Corporate Tax rate on qualifying income, ensure proper segregation of qualifying and non-qualifying income, and review compliance with tax grouping rules and transfer pricing regulations.
10. Are Free Zone companies subject to VAT audits in the UAE?
Yes, Free Zone companies that are registered for VAT (Value Added Tax) in the UAE are subject to VAT audits, either as part of their external financial audit or through separate audits conducted by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). Auditors will verify the accuracy of VAT calculations, returns, and compliance with VAT legislation.
11. What are common challenges faced during a Free Zone external audit?
Common challenges during a Free Zone external audit include ensuring compliance with specific Free Zone bylaws, navigating complex related party transactions, demonstrating economic substance for ESR compliance, properly segregating income for Corporate Tax purposes, and maintaining accurate and comprehensive financial records.
12. What is the role of a firm like ProAct in a Free Zone audit?
Firm like ProAct plays a crucial role by facilitating independent assurance on your financial statements, ensuring compliance with Free Zone regulations and UAE laws, identifying potential risks, offering strategic advisory, and helping you optimize your financial processes. We act as your trusted partner, guiding you through the complexities of Free Zone audits.
13. Can a Free Zone company change its financial year-end?
A Free Zone company may be able to change its financial year-end, but this typically requires prior approval from the relevant Free Zone authority and often the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) for Corporate Tax purposes. It’s essential to consult with your auditor and the Free Zone authority before making any such changes.
14. How long does a typical Free Zone external audit process take?
The duration of a typical Free Zone external audit process varies depending on the size and complexity of the company, the quality of its financial records, and the responsiveness of its management. On average, it can take anywhere from 2 weeks to 2 months from the start of fieldwork to the finalization of the audit report.
15. What are “related party transactions” in the context of Free Zone audits?
Related party transactions refer to dealings between a Free Zone entity and parties that have a significant influence over it, or over which it has significant influence (e.g., parent companies, subsidiaries, common shareholders, key management personnel). Auditors scrutinize these to ensure they are conducted at arm’s length (market rates) and are properly disclosed in the financial statements.
16. How can a Free Zone company prepare for a smooth external audit?
To prepare for a smooth external audit, a Free Zone company should maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records, ensure all supporting documentation is organized, reconcile bank accounts regularly, comply with all Free Zone regulations, address any ESR or Corporate Tax compliance issues proactively, and engage with their chosen audit firm well in advance.
17. What are the benefits of choosing ProAct as your partner?
Choosing ProAct offers numerous benefits, including in-depth knowledge of specific Free Zone bylaws, up-to-date understanding of evolving UAE regulations (ESR, Corporate Tax), proactive risk identification, strategic financial advice, facilitates efficient audit processes, and the assurance of compliance specific to your operating environment.
18. Do startups in Free Zones also need to undergo external audits?
Yes, even startups operating in UAE Free Zones are typically required to undergo annual external audits, regardless of their revenue or operational scale. While smaller startups might qualify for IFRS for SMEs, the audit mandate generally applies to all licensed entities to ensure compliance with Free Zone regulations and maintain license validity.
19. What is the cost of a Free Zone external audit in the UAE?
The cost of a Free Zone external audit in the UAE varies significantly based on factors such as the Free Zone, the size and complexity of the company, the volume of transactions, the industry, and the chosen audit firm. It’s best to request a customized quote after an initial assessment of your specific needs. ProAct offers competitive and transparent pricing for its comprehensive Free Zone audit services.
Free UAE Free Zone Audit Checklist: Is Your Business Audit-Ready?”
Download ProAct’s UAE Free Zone Audit Checklist to identify requirements to stay Audit-Ready.
Click Here! to download
Disclaimer
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, tax, or financial advice. The regulatory environment in the UAE, particularly concerning Free Zones and taxation, is subject to change. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy as of the date of publication, readers should not rely solely on this information. For specific guidance tailored to your business and jurisdiction, it is strongly recommended to consult directly with ProAct’s qualified experts. ProAct disclaims any liability for any actions taken or not taken based on the contents of this article.
If you need to know more details about ProAct’s Freezone Auditing Services in the UAE – Contact us now!
Author Bio:
Written By,


